.jpg)
Basic Life Support (BLS) and Emergency First Aid at Work
Basic Life Support (BLS) Course Content:
Introduction to BLS:
- Definition and importance of Basic Life Support.
- When and where BLS skills might be needed (home, work, public spaces).
Understanding the Chain of Survival:
- Recognition of emergency situations.
- Importance of early CPR and defibrillation.
- Advanced care and post-resuscitation care.
Assessing the Situation and Initial Response:
- Checking the scene for safety.
- Assessing the responsiveness of the person.
- Shouting for help and calling emergency services.
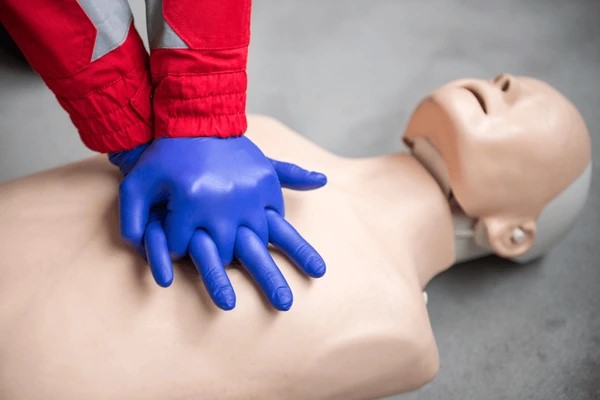
Performing CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation):
- Chest compressions: correct hand placement, depth, and speed.
- Rescue breathing: technique for adults, children, and infants.
- Hands-only CPR for those uncomfortable with mouth-to-mouth.
Using an Automated External Defibrillator (AED):
- How an AED works and when to use it.
- Step-by-step guidance on operating an AED.
- Safety precautions while using an AED.
Managing Choking Emergencies:
- Recognizing signs of choking (adults, children, and infants).
- Techniques for clearing the airway (back blows, abdominal thrusts).
- Special considerations for different age groups.
Recovery Position:
- When and how to place someone in the recovery position.
- Importance of maintaining a clear airway.
Practical Sessions:
- Hands-on practice of CPR and using an AED.
- Simulation of real-life scenarios to build confidence and competence.
Emergency First Aid at Work Course Content:
Introduction to First Aid:
- Importance of first aid in the workplace.
- Legal requirements and responsibilities of first aiders.
Roles and Responsibilities of a First Aider:
- Understanding duties and priorities in an emergency situation.
- Communicating effectively during emergencies.
Assessment of the Scene and Casualty:
- Conducting a primary survey (DR ABC: Danger, Response, Airway, Breathing, Circulation).
- Performing a secondary survey if needed.
Treating Unconsciousness:
- Causes and signs of unconsciousness.
- Steps to take when someone is unresponsive but breathing.
Treating Minor Injuries:
- Cuts, grazes, and bruises.
- Burns and scalds: recognizing severity and providing care.
- Sprains, strains, and minor fractures.
Benefits
Benefits for Individuals:
Life-Saving Skills:
- Provides individuals with the confidence and ability to act quickly and effectively in emergency situations, potentially saving lives.
- Enables them to perform CPR, use an AED, and manage basic first aid needs, which can be critical before professional help arrives.
Increased Confidence in Emergencies:
- Equips people with the knowledge to remain calm and act decisively during accidents or medical emergencies, reducing panic.
- Empowers them to assist family members, friends, or even strangers in need of urgent care.
Career Advancement:
- Adds valuable skills to an individual's resume, making them more attractive candidates for employers, especially in industries where safety is a priority.
- Required or preferred for certain roles, including healthcare professionals, safety officers, and teachers.
Preparedness in Daily Life:
- Useful not only in the workplace but also in everyday situations, such as at home, during travel, or in public spaces.
- Increases awareness of potential hazards and how to mitigate risks in various environments.
Benefits for Industries:
Enhanced Workplace Safety:
- Trained employees can quickly respond to workplace incidents, reducing the severity of injuries and potentially saving lives.
- Promotes a safer work environment, minimizing accidents and ensuring that emergencies are managed effectively.
Compliance with Legal Requirements:
- In many industries, having staff trained in BLS and first aid is a legal requirement. Compliance helps avoid penalties and ensures the organization meets safety standards.
- Ensures readiness for health and safety audits, showing commitment to employee welfare.
Reduced Downtime and Costs:
- Quick response to accidents can prevent minor injuries from becoming severe, reducing time off work and medical expenses.
- Lowers the cost associated with workers' compensation claims, emergency medical services, and potential legal issues.
Improved Employee Morale and Confidence:
- Employees feel safer knowing that their colleagues are trained to handle emergencies, boosting morale and productivity.
- Demonstrates the company’s commitment to the well-being of its workforce, fostering trust and loyalty.
Positive Reputation:
- Companies that prioritize safety and employee training build a strong reputation, which can attract clients, partners, and talent.
- Showcases the organization as a responsible employer who values safety, health, and compliance.
.png)